|
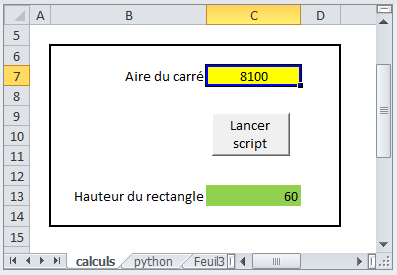
Now let's go back to the excel workbook, there are two cells: the yellow one in C7 and the green one in C13 on a sheet called calculations.
Let's create a new sheet that we're going to call python, but the name doesn't matter. On the other hand, it is necessary to put: " Python Parameters » top left on A1.
First, you'll put your code in column M by copying to M1 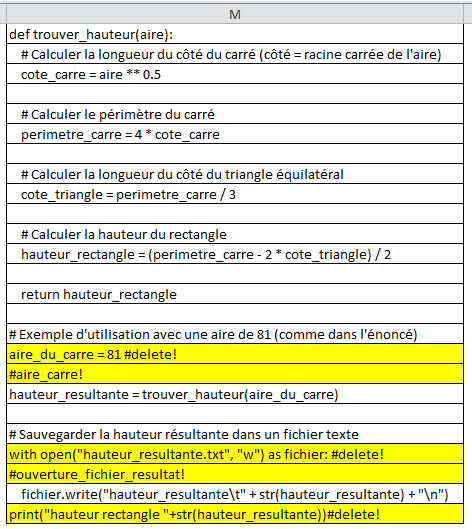
Secondly, you'll define what will replace aire_du_carre=81 To do this you go column F and G and you make the formula for it: in column F, you put the tag you put in your python code and in G you put a formula referring to the cell containing the area (yellow): ="aire_du_carre=" & calculations! C7 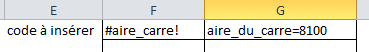 The python language does not consider the comma as a decimal separator, so if you have a computer set to French you can modify the decimal point of the comma. The python language does not consider the comma as a decimal separator, so if you have a computer set to French you can modify the decimal point of the comma.
=SUBSTITUE("aire_du_carre=" & calculs!C7;",";".")
Now you need to add the vba code for the button.
Sub lance_script()
Run "'python.xlsm'!lance_script_python"
End Sub
“pyton.xlsm” is the name of the workbook when it is not installed, when it is in the form of an installed add-in, it will be a name with an .xlam extension.
To assign the macro to the button: right click then assign a macro.
Once the macro is launched, we see the script “script_python.py” is created, the end of which is shown below.
aire_du_carre=8100
hauteur_resultante = trouver_hauteur(aire_du_carre)
# Sauvegarder la hauteur résultante dans un fichier texte
with open('D:/projets/Simulation/resultat.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as fichier:
fichier.write("hauteur_resultante\t" + str(hauteur_resultante) + "\n")
|